- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Controller General of Accounts (CGA)
Controller General of Accounts (CGA)
03-06-2024
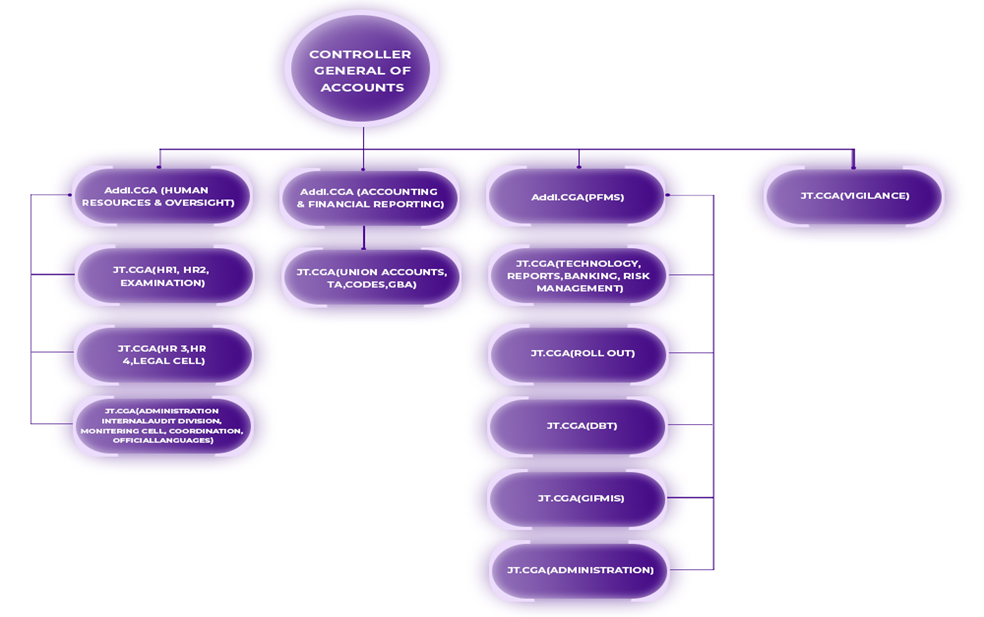
The Controller General of Accounts (CGA) serves as a key unit in the financial management system of the Government of India.
- Established in October 1975 under the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance.
- CGA plays a role in ensuring fiscal discipline and transparency.
Key Functions and Responsibilities of CGA:
- Principal Accounting Adviser: The CGA is the government's principal accounting adviser, providing guidance and support on various fiscal matters.
- Establishment and Management of Accounting System: The CGA is responsible for establishing and managing a robust Management Accounting System for the Union Government, ensuring accurate and efficient financial reporting.
- Preparation and Submission of Accounts: The CGA is entrusted with the preparation and submission of the Union Government's accounts, ensuring compliance with established accounting principles and procedures.
- Exchequer Control and Internal Audits: The CGA is tasked with maintaining exchequer control and conducting internal audits for the central government, safeguarding public funds and promoting accountability.
- Analysis of Fiscal Indicators: The CGA prepares annual analyses of expenditure, revenues, borrowings, and fiscal indicators for the Union Government, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making.
- Formulation of Accounting Policies: The CGA formulates accounting policies and procedures for both the Central and State Governments, ensuring uniformity and consistency in financial reporting.
- Administration of Payments, Receipts, and Accounting: The CGA plays a central role in the administration of payments, receipts, and accounting in Central Civil Ministries and Departments, facilitating efficient financial management.
- Monitoring of Technical Standards: Through its internal audit units, the CGA ensures compliance with required technical standards of accounting in the departmental accounting offices and monitors the financial performance of various Government programmes and schemes.
- Banking Arrangements and Reconciliation of Cash Balances: The CGA administers banking arrangements for government expenditures and collections, facilitating smooth financial transactions. It also interacts with the Central Bank to reconcile the cash balances of the Union Government.
- Monitoring of Corrective Actions: The CGA monitors the progress of corrective actions taken on recommendations made by the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) and the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) through its web-based Audit Para Monitoring System (APMS).
- Management of Central Government Pensions: The CGA is responsible for the management of pensions for Central government employees, ensuring timely and accurate disbursement of retirement benefits.
Public Accounts Committee (PAC):
- The Public Accounts Committee (PAC) is a parliamentary committee constituted to audit the revenue and expenditure of the Indian government.
- Comprising not more than 22 members, 15 elected from the Lok Sabha and 7 from the Rajya Sabha.
- The PAC serves as a vital check on the executive branch of the government, ensuring accountability and transparency in fiscal matters.
In conclusion, the Controller General of Accounts (CGA) plays an important role in ensuring prudent financial management and accountability in the Indian government. Through its wide range of functions and responsibilities, the CGA contributes significantly to the effective utilization of public funds and the promotion of fiscal discipline.
Must Check: UPSC Coaching Institute In Delhi



