- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Conocarpus Tree
Conocarpus Tree
22-11-2023

Context :
Recently in October 2023, various concerns over the mismanagement of the Conocarpus species (invasive) of trees have led Gujarat to ban their use.

What are Invasive species of trees?
Invasive alien species which are also known as non-native species, refer to organisms which have been introduced to the ecosystems outside of their native ranges and have established self-sustaining colonies. These organisms often outcompete native species and disturb the balance of the ecosystem, leading to a variety of harmful impacts.
What are the threats associated with them?
- Biodiversity Disruption: Eucalyptus, introduced for timber, often forms monocultures, reducing biodiversity and altering soil composition.
- Water Depletion: Some invasive trees, like Prosopis juliflora [ Vilayti Kikar ], consume excessive water, leading to reduced groundwater levels. This poses a threat to local water resources and affects the livelihoods of communities dependent on agriculture.
- Fire Hazard: Certain invasive species, such as Acacia mearnsii, are highly flammable, increasing the risk of wildfires. These fires can devastate natural habitats, destroy native vegetation, and impact wildlife.

- Altered Soil Chemistry: Invasive trees can alter soil nutrient levels, impacting the growth of native plants. Lantana camara, for example, releases chemicals that inhibit the germination and growth of surrounding vegetation, affecting the composition of the forest floor.
- Economic Impact: Invasive species can have economic repercussions by affecting agriculture and forestry. For instance, the widespread invasion of the invasive weed Parthenium hysterophorus has led to significant losses in crop yield and poses a threat to livestock health.
Why is there a rise in such exotic species?
- Global Trade and Transportation: Increased global trade has facilitated the unintentional introduction of invasive tree species through cargo shipments and transportation networks.
- Agricultural Practices: Modern agricultural practices and afforestation projects sometimes introduce non-native tree species without considering their potential invasiveness.
- Climate Change: Shifting climatic conditions may create more favorable habitats for certain invasive tree species, allowing them to thrive and outcompete native vegetation.
How to manage this menace?
- Early Detection and Rapid Response: Implement vigilant monitoring systems to identify invasive tree species early, enabling prompt containment and eradication measures.
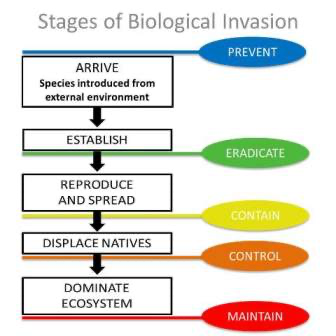
- Public Awareness and Education: Conduct outreach programs to educate communities about the ecological threats posed by invasive trees, fostering public participation in eradication efforts. Eg ; Campaign against Vilayati Kikar in Delhi.
- Legislation and Regulation: Strengthen and enforce policies that regulate the import, sale, and cultivation of potentially invasive tree species to prevent their introduction and spread.
- Research and Development: Invest in scientific research to understand the biology and behavior of invasive trees, facilitating the development of effective control methods and strategies.
- Collaborative International Efforts: Engage in cross-border collaborations to share information, resources, and expertise, creating a unified front against the transboundary spread of invasive tree species in India. Eg ; under the 2022 Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework , the member governments have committed to reduce the introduction and establishment of all exotic alien species by at least 50% by 2030.
Therefore, by developing a comprehensive national strategy, incorporating scientific insights, community engagement, and stringent regulations, we can mitigate the spread of invasive tree species and protect India's diverse ecosystems.



