- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Choline: An Essential Nutrient for Bodily Functions
Choline: An Essential Nutrient for Bodily Functions
10-05-2024
Recent research has revealed the important role of a protein called FLVCR2 in delivering an essential nutrient called choline to the brain.
What is Choline?
- Definition and Functions:
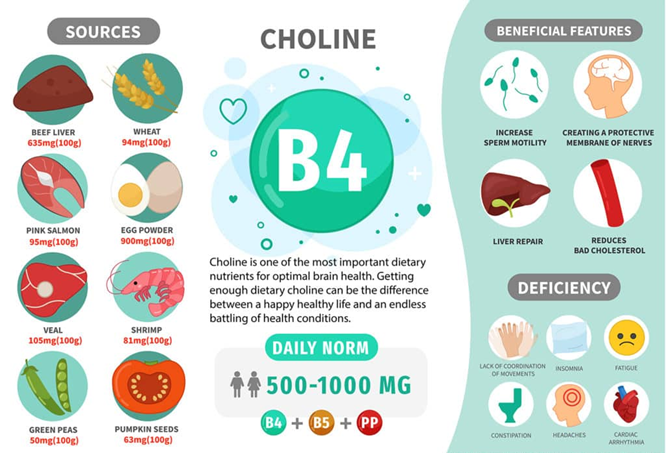
- Choline is an important nutrient involved in various bodily functions, including cell growth and metabolism.
- It exists in both water-soluble and fat-soluble forms, affecting its transport and absorption by the body.
- Production and Dietary Sources:
- The body produces small amounts of choline in the liver, but it's not enough to meet daily requirements.
- Dietary sources of choline include meat, fish, dairy, eggs, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Functions and Roles:
- Cell Structure: It's a part of phospholipids, lipids that form structural components of cell membranes, ensuring their integrity.
- Methyl Group Source: Choline serves as a source of methyl groups, which are essential for various metabolic processes.
- Liver Health: It's required to clear cholesterol from the liver, preventing fat and cholesterol buildup that could lead to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Neurotransmitter Production: Choline is important for making acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory, muscle movement, heartbeat regulation, and other essential functions.
- Gene Expression and Signaling: Choline plays a role in modulating gene expression, cell membrane signaling, lipid transport and metabolism, and early brain development.
- Gut Health: Choline also serves as nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria.
- Health Implications of Deficiency:
- Choline deficiency can lead to health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and muscular damage.
- What are Neurotransmitters?
- Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers crucial for cell-to-cell communication within the nervous system.
- They transmit signals from one neuron to another, muscle cells or glands.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



