- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
BORDER INFRASTRUCTURE
BORDER INFRASTRUCTURE
20-10-2023

Context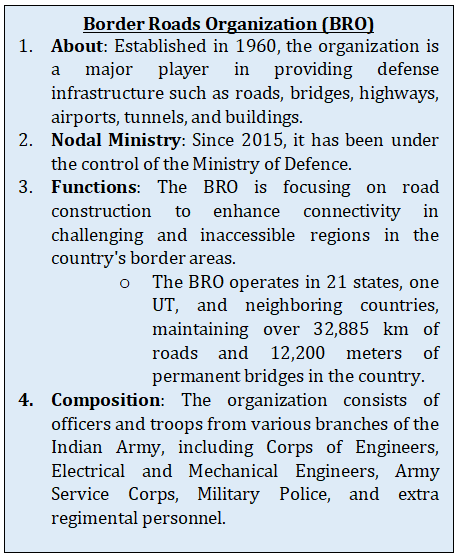
- In September 2023, India's Defence Minister inaugurated several projects of the Border Road Organisation to enhance the country's border infrastructure.
More in News
- The projects have been constructed in the border regions of 11 Indian states and union territories.
- The border infrastructure includes airfields, tunnels, all-weather roads, fencing, and the construction of new railway lines.
What are the Important projects constructed under Border Infrastructure Developments?
- Devak Bridge: The 422.9-meter long bridge in Jammu, located near the Indo-Pak international border, is situated on the Bishnah-Kaulpur-Phulpur Road.
- Nechiphu Tunnel: The Nechiphu Tunnel, located on Balipara-Chariduar-Tawang Road in Arunachal Pradesh, will offer all-weather connectivity to the strategic Tawang Region, alongside the ongoing Sela Tunnel.
- Bagdogra and Barrackpore Airfields: The airfields in West Bengal, costing over Rs 500 crore, will enhance the Indian Air Force's readiness and facilitate commercial flight operations in the region.
- Nyoma Airfield: The airfield in Eastern Ladakh, estimated to cost around Rs 200 crore, will enhance the air infrastructure in Ladakh and enhance IAF's Northern border capability.
What are the Neighborhood Projects under Border Infrastructure Developments?
- Nepal: The Motihari - Amlekhgunj Pipeline, South Asia's first cross-border petroleum products pipeline, is being built with Indian grant assistance over the Mahakali River.
- Bangladesh: The Maitri Setu High Speed Diesel pipeline, in collaboration with Bangladesh, aims to decrease petrol prices and alleviate road congestion.
- Myanmar: The Sittwe port project and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP) are significant initiatives in the transportation sector.
- Bhutan: The Indian government is granting a grant to develop a dry port in Pasakha, which is located near West Bengal.
What is the Need/ Importance of Border Infrastructure Developments?
- To Address Porous borders: India is grappling with persistent territorial and boundary disputes with China and Pakistan, as well as porous borders along challenging terrain.
- For example: The ongoing standoff along the LAC since April 2020, resulting in clashes with the Chinese People's Liberation Army, has led to numerous skirmishes.
-
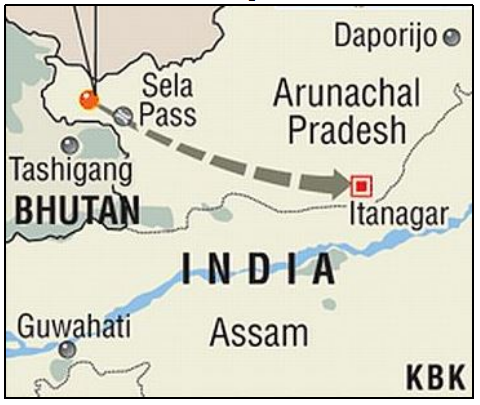
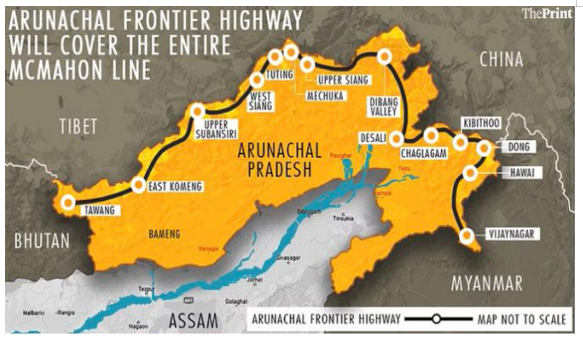
- Strengthening infrastructure: India's borders face inadequate infrastructure despite border wars, with multiple military, para-military, and police forces operating in discord and lack of coordination.
- Surveillance: Smugglers, drug traffickers, and terrorists often take advantage of poor surveillance and infrastructure at borders.
- To Adopt Multi-Pronged Approach: To enhance the connection to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) via roads, bridges, and tunnels.
- To enhance cross-border connectivity between neighboring countries through various infrastructure such as highways, bridges, inland waterways, railroads, electricity lines, and fuel pipelines.
- Modernizing and constructing Integrated Check Posts at border crossings to facilitate trade, as well as funding and constructing infrastructure projects in neighboring countries.
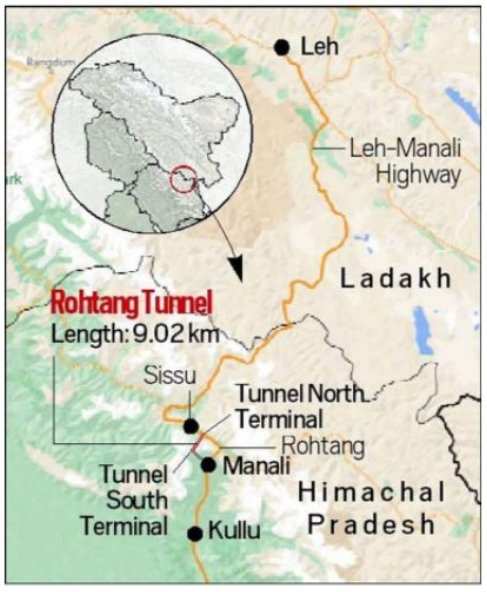
What is the Issue/ Concerns/ Challenges in creating border infrastructure?
- Challenging Geographical Terrain: India's international border spans across various terrains such as marshy lands, salt pans, deserts, valleys, rivers, and forests.
- Political instability: Political instability in neighboring countries like Pakistan can lead to border-related issues, causing mass migrations and other potential issues.
- Lack of cooperation: The Lack of Coordination between Home Affairs and Defence Ministries has resulted in significant infrastructure delays in the border areas.
- Radicalization: Economic underdevelopment in border areas often leads to the lack of essential infrastructure, making them potential hotspots for radicalization.
- Ex: The northeastern states are grappling with ethnic conflicts and regional separatist forces, which pose significant challenges to the development of border infrastructure.
- Porous borders: They facilitate criminal activities such as smuggling, human trafficking, drug and weapon trafficking, and infiltration in border regions.
- Environmental concerns: Large infrastructure projects in ecologically sensitive areas may cause biodiversity damage, and highway projects within 100 km of India's "Line of Control" are exempt from environmental clearances.
- Lack of funds': The Home Ministry's parliamentary committee is concerned about the underutilization of funds for border infrastructure and development programs.
What are the initiatives taken by the government to Strengthen Border infrastructure?
- Border Area Development Programme (BADP): BADP, initiated during the Seventh Five Year Plan (1985-90), aims to balance development in western border areas by promoting infrastructure and security for remote, inaccessible populations.
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS): Advanced surveillance technologies like thermal imagers, infra-red alarms, aerostats, ground sensors, radars, sonar systems, fiber-optic sensors, and a real-time command-and-control system are deployed to secure borders.
- BOLD-QIT, a Border Electronically Dominated QRT Interception Technique, is being utilized under CIBMS on the Indo-Bangladesh border in Dhubri district of Assam.
- Vibrant Villages Programme: The Vibrant Villages Programme, announced in the 2022-23 Budget, aims to address border villages with limited connectivity and infrastructure, including construction of infrastructure, housing, tourist centers, and livelihood support.
- Border Infrastructure and Management (BIM): It is a Central Sector Umbrella Scheme which aims to provide better roads, electricity, and communication infrastructure along the border areas.
- Shekatkar Committee's recommendations: The Committee's recommendations on border infrastructure, including outsourcing road construction, introducing modern construction plants, land acquisition, and obtaining statutory clearances, are being implemented.
Way Forward
- Ground level participation: There is a need to involve local communities in border management, acting as observers and listeners for the forces, to enhance border surveillance.
- Strengthening open borders: To decrease the distance between inter-border outposts across open borders to decrease trafficking, smuggling, and counterfeit currency cases.
- Strengthening Security forces: To improve the efficiency of border security forces by upgrading their technology for effective patrolling and monitoring of the border region.
- Utilization of Technology: Utilize technology like LIDAR, Laser Fencing, flood lightings, CCTVs, and drone surveillance to create a Border Protection Grid in every border state.
- Inventory Upgradation: The current inventory of equipment and accessories is being continuously upgraded in line with the new project to ensure optimal utilization.
- Private sector participation: Encouraging private sector participation in technological upgradation and maintenance of electronic and surveillance equipment is crucial.
- Collaboration with neighboring countries: There is a need to foster cooperation with neighboring nations to develop mutually beneficial infrastructure projects and enhance economic and cultural exchange to strengthen relationships and foster trust.
- Improve connectivity: The investment in telecommunications and transportation networks aims to enhance connectivity with neighboring nations.
- Adequate Investment: Investment in physical infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and border infrastructure, is being continued in regions along the Chinese border.



