- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) Technology
Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) Technology
08-05-2024

The AIP system is important for the Indian Navy to keep vessels underwater for longer periods and enable submarine fleet to have bigger vessels with more advanced capabilities.
- Rs 60,000 crore contract to modernise the Indian Navy submarine fleet to build 6 stealth submarines equipped with Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) technology, enabling prolonged underwater operations, has started with trials of competing teams at Mazgaon Docks, Mumbai.
- The project 75 of the Indian Navy aims to procure diesel- electric attack submarines with fuel cells equipped with AIP technology to replace the aging fleet for new combat roles.
What is AIP?
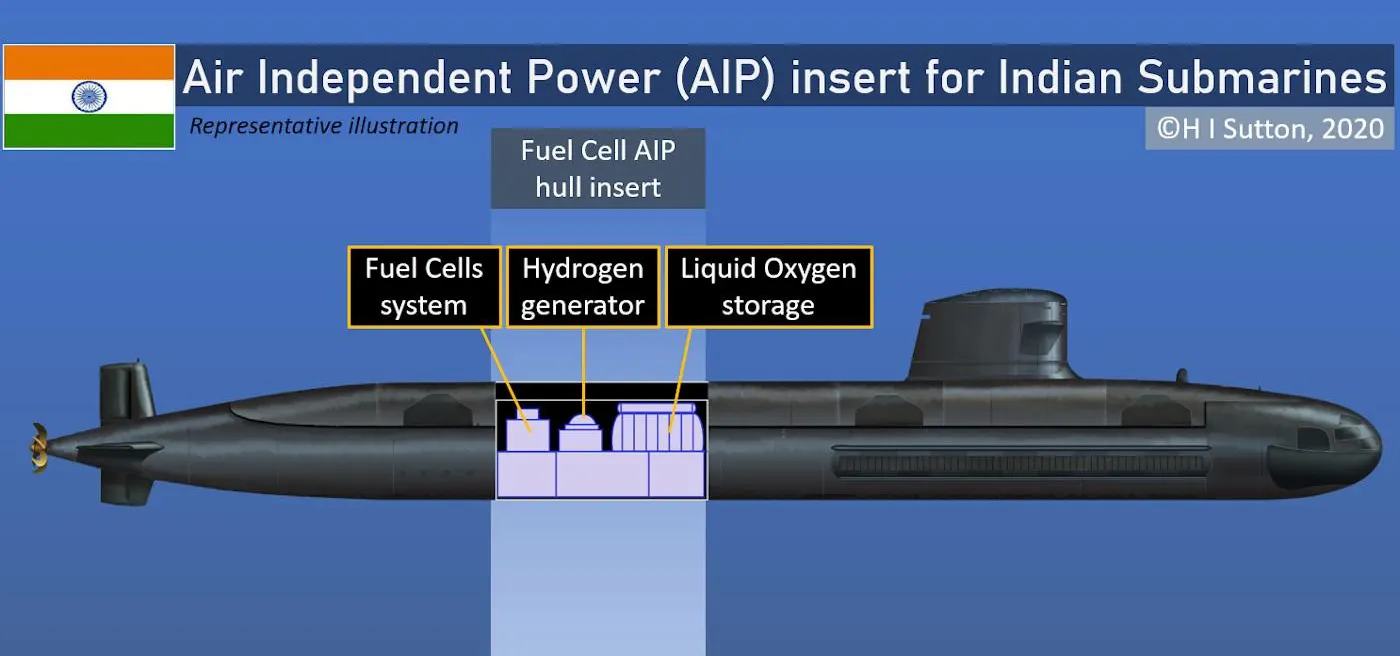
What is Air Independent Propulsion (AIP)?
- Submarine Enhancement: Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) is a technology that allows non-nuclear submarines to operate without needing to surface to access atmospheric oxygen.
- Extended Underwater Endurance: Traditional diesel-electric submarines need to surface frequently to recharge their batteries using diesel engines (which require air). AIP extends submerged operation times from a few days to several weeks.
- Stealth Advantage: Since AIP submarines can stay submerged longer, they are significantly harder to detect, giving them a tactical advantage.
Advantages of AIP
- Increased Submerged Time: The primary benefit of AIP is dramatically increasing the time a submarine can stay underwater.
- Enhanced Stealth: AIP reduces the need to surface, minimizing a submarine's vulnerability to detection.
- Improved Operational Range: Longer underwater endurance allows AIP-equipped submarines to cover greater distances without surfacing.
Types of AIP:
- Open-cycle systems
- Closed-cycle diesel engines
- Closed-cycle steam turbines
- Stirling cycle engines
- Fuel cells
DRDO's Fuel Cell-based AIP System:
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is developing a unique fuel cell-based AIP system.
- It generates hydrogen onboard, enabling endurance and maximum power modes as per user requirements.
- Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL) of DRDO is responsible for developing this system.
Types of Submarines:
- Conventional or Diesel-electric submarine: Requires atmospheric oxygen to run the diesel generator, which charges the batteries.
- Nuclear Submarine: Powered by a nuclear reactor, not necessarily nuclear-armed. Offers significant performance advantages over conventional submarines.
Nuclear Submarines:
- Nuclear submarines are naval vessels powered by nuclear reactors for propulsion.
- They may or may not carry nuclear weapons.
- The history of nuclear submarines dates back to the 1950s, with the US developing the first nuclear submarine, USS Nautilus, in 1954.
- Subsequently, Russia, France, Britain, China, and India engaged in nuclear submarine technologies.