- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
AFRICA'S AFAR TRIANGLE: A RIFT VALLEY OF GEOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
AFRICA'S AFAR TRIANGLE: A RIFT VALLEY OF GEOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
06-04-2024
- Geologists have made a discovery in the Afar Triangle of Africa, which is known for its geological importance.
- A fault has been discovered, indicating the possible formation of the world's sixth ocean in the future.
- This phenomenon is driven by tectonic plate movements, particularly in the East African Rift System.
Causes of the Rift:
- This rift is the result of the separation of tectonic plates, which is expected to split the African continent in about 5 to 10 million years.
- This separation would create a new ocean basin, significantly changing the geography of the area.
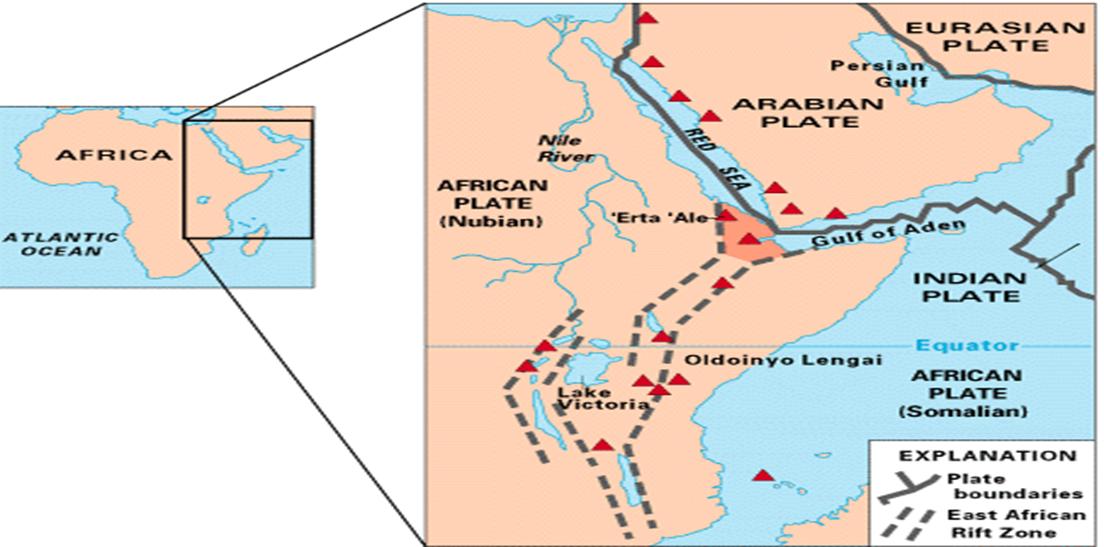
About the Afar Triangle:
- The Afar Triangle is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa.
- It extends across Eritrea, Djibouti and the Afar region of Ethiopia, and includes Lake Assal, the lowest point in Africa.
- The region is characterized by extreme heat and drought, with temperatures among the hottest on Earth.
- It is bordered by the Ethiopian Plateau, Danakil Block, Somali Plateau and Ali-Sabih Block.
Fossil Discoveries:
- There have been important fossil discoveries related to early hominin and human tool culture in the Afar region.
- Sites like Hadar and Dikika have provided valuable insights into our evolutionary origins.
The Current 5 Oceans on Earth:
- Pacific Ocean (largest)
- Atlantic Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- Southern Ocean
- Arctic Ocean (smallest)
FAQs:
Q. What is tectonic plate movement?
Ans. Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how the Earth's underground movements create major landforms. It describes a global system of boundaries associated with mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones, and transform faults on Earth.

The theory states that Earth's lithosphere is composed of several large tectonic plates that have been slowly moving for about 3.4 billion years. The plates move due to the relative density of the oceanic lithosphere and the relative weakness of the asthenosphere.
The location where two plates meet is called a plate boundary. There are three types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform.
- A divergent boundary is where two plates move away from each other. This creates a gap between the plates, causing magma to fill the gap and produce a new crust.
- A convergent boundary is where two plates come together.
- A transform plate boundary is a fault where tectonic plates slide past each other horizontal
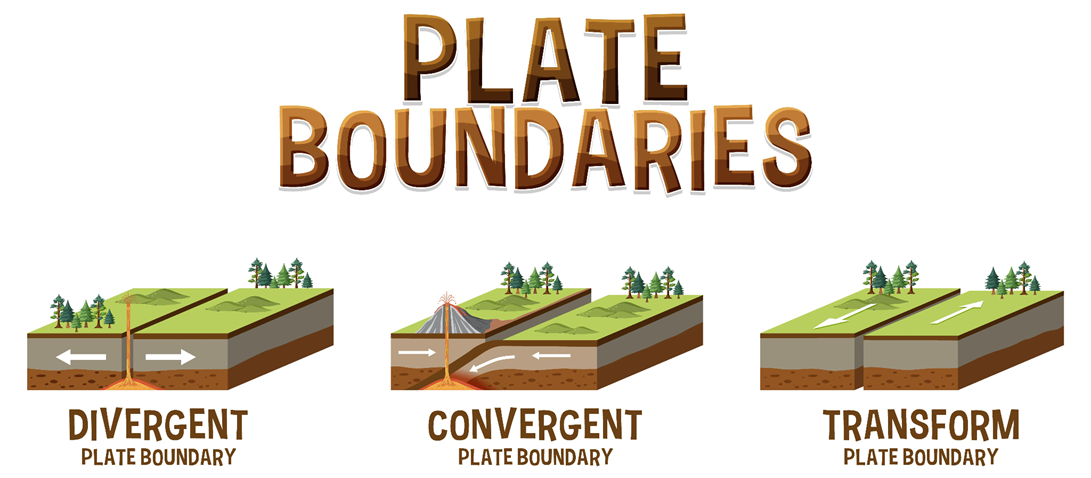
Plate boundaries are commonly associated with geological events such as earthquakes and the creation of topographic features such as mountains, volcanoes, and mid-ocean ridges
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



