- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
6th BIMSTEC Summit
6th BIMSTEC Summit

- In the 1st week of April 2025, The 6th BIMSTEC Summit was hosted by Thailand 3 years after the previous (virtual) summit in 2022.
- Thailand is currently serving as the chair of the BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) organization.
- Theme 2025: The theme of the summit was "BIMSTEC: Prosperous, Resilient, and Open."
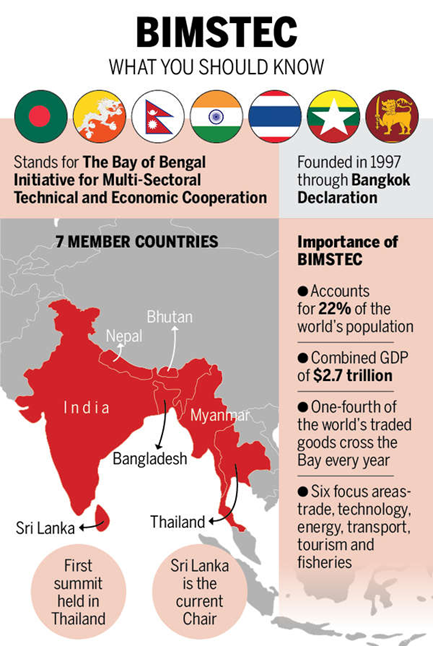
About BIMSTEC:
|
Establishment |
06 June 1997, with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration |
|
Initial Name |
BIST-EC (Bangladesh-India-Sri Lanka-Thailand Economic Cooperation) |
|
Initial Members |
Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand signed the Bangkok Declaration on 06 June 1997 |
|
Primary Aim |
Promotion of economic cooperation among countries bordering the Bay of Bengal |
|
Expansion of Membership |
- Myanmar joined on 22 December 1997, renamed to BIMST-EC - Nepal and Bhutan admitted in July 2004 |
|
Renaming to BIMSTEC |
During the First Summit in Bangkok on 31 July 2004, renamed to Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) |
|
Members |
Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and Thailand |
|
Representation |
Represents over 1.7 billion people, approximately 22% of the global population |
|
GDP |
Combined GDP of the member countries is approximately USD 4.5 trillion |
|
Permanent Secretariat |
Located in Dhaka, Bangladesh |
How Chairmanship Rotates?
- The leadership of BIMSTEC changes every 2 years, based on the alphabetical order of the country names in English.
- After Thailand, it was Bangladesh’s turn.
- So, on 4 April 2025, Bangladesh officially became the new Chair of BIMSTEC for the next 2 years.
- Moreover , Chief Advisor of Bangladesh, Muhammad Yunus, accepted the chairmanship.
Previous BIMSTEC Summits:
|
No. |
Date |
Host country |
|
3rd |
4 March 2014 |
Myanmar |
|
4th |
30–31 August 2018 |
Nepal |
|
5th |
30 March 2022 |
Sri Lanka |
|
6th |
4-6 April 2025 |
Thailand |
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Participation:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi actively participated in the summit.
- However, he presented a comprehensive 21-point action plan designed to enhance cooperation and collaboration among BIMSTEC member nations.
|
About Tipitaka (World Tipitaka)
|
Prime Minister’s Address at the Summit:
Opening Remarks:
- PM Modi began by expressing heartfelt gratitude to Prime Minister Her Excellency Shinawatra and the Government of Thailand for organizing the summit efficiently and effectively.
- Additionally, On behalf of the people of India, PM Modi conveyed his sincere condolences for the lives and properties lost due to the recent earthquake in Myanmar and Thailand.
- He emphasized that BIMSTEC is an important link between South and Southeast Asia.
- And it is steadily evolving into a robust platform for regional cooperation, economic growth, and shared prosperity among its members.
- PM Modi also mentioned that the BIMSTEC Charter came into force the previous year.
- And he also expressed confidence that the Bangkok Vision 2030 would help the Bay of Bengal region to become more prosperous, secure, and inclusive in the future.
Proposals for Strengthening BIMSTEC:
- Institutional Strengthening:
- PM Modi highlighted the need to expand the role of BIMSTEC and enhance its institutions.
- He specifically noted the establishment of a Home Ministers' Mechanism.
- It is expected to play an important role in addressing critical regional issues like cybercrime, terrorism, drug trafficking, and human trafficking.
- India also proposed hosting the first meeting of this mechanism later in the year, further strengthening the region’s collective security.
- Connectivity Initiatives:
- PM Modi highlighted physical, digital, and energy links within the BIMSTEC region as essential for promoting regional progress.
- He mentioned that the BIMSTEC Energy Centre based in Bengaluru had already started its operations.
- Furthermore, he proposed accelerating efforts to establish an electric grid connection across the region.
- India shared its Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) expertise and suggested conducting a study to identify the specific needs of BIMSTEC countries in this domain.
- Linking payment systems, especially by connecting India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with those of other BIMSTEC countries, was also suggested as a means to facilitate smoother trade, business, and tourism across the region.
- Economic Connectivity:
- PM Modi proposed the creation of a BIMSTEC Chamber of Commerce and the organization of an annual BIMSTEC Business Summit to enhance economic ties among member states.
- He also suggested exploring a feasibility study to investigate the possibility of conducting trade in local currencies among BIMSTEC countries, further enhancing economic integration.
- Maritime and Security Cooperation:
- PM Modi reiterated the shared commitment to ensuring a free, open, and secure Indian Ocean.
- The Maritime Transport Agreement signed during the summit is expected to improve cooperation in shipping and cargo transport.
- India proposed establishing a Sustainable Maritime Transport Centre.
- It would focus on capacity building, research, innovation, and better coordination on maritime security policies in the region.
- Disaster Management and Public Health:
- Acknowledging the region’s vulnerability to natural disasters, particularly in light of the recent earthquake, PM Modi proposed the establishment of a BIMSTEC Centre of Excellence for Disaster Management.
- This centre would aim to improve disaster preparedness, relief efforts, and recovery strategies.
- India also committed to hosting the 4th Joint Exercise for BIMSTEC Disaster Management Authorities later in the year, which would enhance regional disaster management capabilities.
- PM Modi reiterated India’s commitment to supporting cancer care training in BIMSTEC countries and establishing a Centre of Excellence to promote research on traditional medicine in the region.
- He suggested creating a Centre of Excellence in India to share agricultural knowledge, promote research, and enhance skills for farmers across BIMSTEC countries.
- Scientific and Technological Cooperation:
- India also offered to share its space expertise.
- It includes providing training for personnel, developing nano-satellites, and using remote sensing data to support BIMSTEC countries in their scientific and technological endeavors.
- Youth Development and Cultural Initiatives:
- PM Modi proposed launching the BODHI (BIMSTEC for Organized Development of Human Resource Infrastructure) initiative.
- It would train 300 young people annually from BIMSTEC countries in India, with a focus on skills development.
- India will offer scholarships for BIMSTEC students at India’s Forestry Research Institute and expand the scholarship opportunities at Nalanda University.
- Additionally, an annual training program for young diplomats from BIMSTEC countries will also be organized.
- PM Modi emphasized the shared cultural heritage within the BIMSTEC region, citing cultural examples like Odisha's Bali Jatra and common Buddhist and Hindu traditions.
- India will host the BIMSTEC Traditional Music Festival later in the year to celebrate this shared heritage.
- India will host the BIMSTEC Young Leaders' Summit and introduce initiatives like the BIMSTEC Hackathon and the Young Professional Visitors Programme to promote innovation and collaboration among the region's youth.
- Sports and Celebrations:
- India will organize the BIMSTEC Athletics Meet in 2025.
- Also India will host the inaugural BIMSTEC Games in 2027, marking BIMSTEC’s 30th anniversary.
- PM Modi concluded his speech by reaffirming that BIMSTEC represents a model of inclusive growth and collective security, reflecting the values of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Prayas” (Together, For Everyone’s Growth, Through Everyone’s Effort).
Key Agreements & Documents Adopted at the Summit:
- This declaration outlines a shared vision and collective commitments to a Prosperous, Resilient, and Open BIMSTEC.
- BIMSTEC Bangkok Vision 2030:
- This comprehensive roadmap sets the direction for BIMSTEC for the next 5 years.
- It is aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Key focuses include:
- Prosperity: Emphasizing trade, sustainable development, and poverty alleviation.
- Resilience: Aiming at enhancing agriculture, public health, and disaster preparedness.
- Openness: Promoting tourism, connectivity, and inclusivity.
- BIMSTEC Maritime Transport Cooperation Agreement:
- It aimed at improving cargo and passenger movement across the Bay of Bengal.
- This agreement establishes a Joint Shipping Coordination Committee and a framework for dispute resolution.
- Rules of Procedure for BIMSTEC Mechanisms:
- It will complement the BIMSTEC Charter (2022).
- Also these rules will also improve the institutional clarity, decision-making processes, and operational coherence within BIMSTEC.
- MoUs with International Organizations:
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA): This MoU enhances external cooperation on maritime and blue economy issues.
- UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime): Strengthens collaboration in counter-narcotics, criminal justice reform, and the prevention of transnational crime.
- Approval of the Eminent Persons Group (EPG) Report:
- The report offers strategic recommendations for BIMSTEC’s future, focusing on:
- Institutional reforms,
- Prioritizing key sectors,
- Long-term visioning for the region.
- The report offers strategic recommendations for BIMSTEC’s future, focusing on:
Key Differences Between BIMSTEC and SAARC:
|
Aspect |
BIMSTEC |
SAARC |
|
Geographical Scope |
Bridges South Asia and Southeast Asia |
Limited to South Asia |
|
Membership |
Excludes Pakistan 7 : Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and Thailand |
Includes Pakistan 8 : Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, and Sri-Lanka |
|
Focus |
Primarily functional (trade, connectivity, disaster management) |
Primarily political, but often stalled due to rivalries |
|
Summits and Progress |
4 summits held since 2016 |
No summits since 2014, leading to inactivity |
|
Sectoral Leadership |
Each member country leads specific sectors (e.g., India in Security, Thailand in Connectivity) |
No sectoral leadership structure |
|
India’s Role |
India’s leadership is well-received |
India’s leadership often hindered by Pakistan’s resistance |
In BIMSTEC, India’s leadership is generally well-received, whereas in SAARC, Pakistan’s resistance has often hindered progress and cooperation.
Challenges Faced by BIMSTEC:
- Despite the signing of an FTA (Free Trade Agreement) in 2004, it remains unimplemented.
- Connectivity initiatives like the Trilateral Highway and Kaladan Project are delayed due to challenges with funding and land acquisition.
- The BIMSTEC Secretariat faces challenges of being understaffed and underfunded, which affects the efficient execution of initiatives.
- The absence of a permanent funding mechanism further hampers the implementation of large-scale projects.
- BIMSTEC operates on a consensus-based model, which at times results in policy paralysis as it becomes difficult to reach agreement on key issues.
- Political instability in Myanmar and other bilateral disputes occasionally disrupt the smooth functioning of BIMSTEC, affecting overall cooperation.
- Despite efforts to implement the FTA, intra-regional trade in BIMSTEC remains below 10% of total trade, indicating limited economic integration within the region.
- BIMSTEC struggles with lower visibility compared to other regional groups like ASEAN, and has faced challenges in garnering adequate public and private sector engagement.
Way Forward for BIMSTEC:
- There is a need to accelerate the implementation of key agreements, such as the FTA and the Coastal Shipping Agreement, to enhance regional integration.
- The BIMSTEC Secretariat should be bolstered with additional staff and resources to improve its operational capacity and effectiveness.
- The BIMSTEC Master Plan for Transport Connectivity needs to be fully implemented, with emphasis on digital infrastructure and the establishment of cross-border power grids.
- Efforts should be made to engage the private sector, civil society, and academia to actively participate and drive initiatives within BIMSTEC.
- BIMSTEC should focus on expanding counter-terrorism, cybersecurity, and maritime security cooperation to strengthen the region's security architecture.






