- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
23rd Meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of Government
23rd Meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of Government
- The 2024 Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (23rd summit of SCO Council of Heads of Government) was held on October 15-16 in Islamabad, Pakistan.
- This meeting was focusing on enhancing multilateral cooperation among member states on key issues such as:
- Combating terrorism
- Economic collaboration
- Climate change
- The 2023 SCO Summit (23rd Summit of the SCO Council of Heads of State) took place on July 4, 2023, in New Delhi.
What is Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)?
- The SCO Summit is an annual meeting where leaders from member countries discuss and coordinate on significant regional issues.
- These summits play a crucial role in strengthening ties and promoting mutual understanding among member nations.
Historical Background:
- The dissolution of the USSR in 1991 raised concerns about extremist religious groups and ethnic tensions in the region.
- In response, a group called (Shanghai Five) was Established in 1996 to address security matters. It was initially established by 5 countries:
- China
- Russia
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- The founding countries signed significant treaties in 1996 and 1997:
- Treaty on Deepening Military Trust in Border Regions (Shanghai)
- Treaty on Reduction of Military Forces in Border Regions (Moscow)
- Between 1998 and 2000, summit meetings were held in Almaty, Bishkek, and Dushanbe to discuss security and various political and economic issues.
- The organization officially transformed into the SCO(An intergovernmental organization) in June 2001, during a meeting in Shanghai, China where Uzbekistan was admitted, and the Shanghai Convention on Combating Terrorism, Separatism and Extremism was signed.
- The SCO Charter was signed on June 7, 2002, in St. Petersburg, outlining its structure and objectives.
Current Membership:
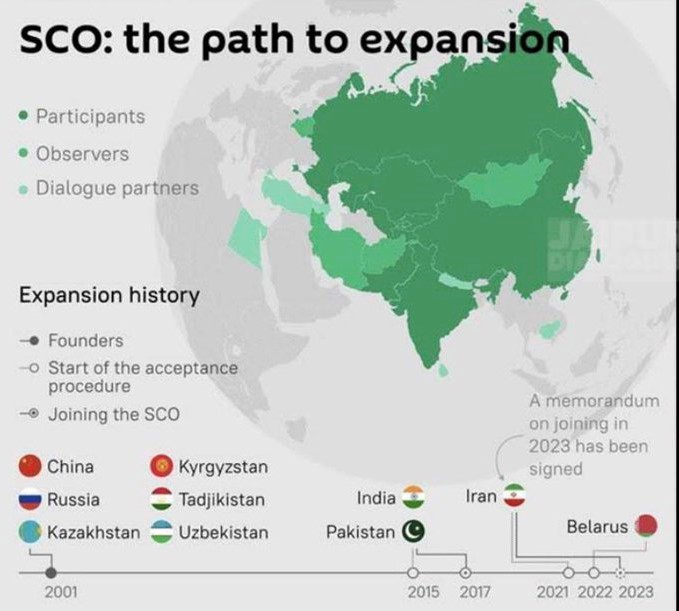
As of 2024, the SCO has 10 full members:
- China
- Russia
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- India (joined in 2017) Approval of India and Pakistan as full members at the 17th SCO Summit
- Pakistan (joined in 2017)
- Iran (joined in 2023)
- Belarus (joined in 2024)
- Belarus was previously a dialogue partner (2010) and an observer state (2015).
Observer States and Dialogue Partners:
Other observer states interested in full membership include Afghanistan and Mongolia. The SCO also has 14 dialogue partners:
- Azerbaijan
- Armenia
- Bahrain
- Egypt
- Cambodia
- Qatar
- Kuwait
- Maldives
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Turkey
- Sri Lanka
India’s Role in SCO
- 2005: India was granted observer status.
- 2015: The SCO decided to admit India and Pakistan as full members at the Ufa Summit in Russia.
- 2016: India and Pakistan signed the memorandum of obligations in Tashkent.
- 2017: India officially joined SCO as a full member at the Astana Summit.
Since becoming a full member, India has focused on:
- Strengthening the SCO's core agenda on terrorism and radicalism.
- Reinforcing commitment to regional connectivity, stability, territorial integrity, and sovereignty.
Objectives of the SCO:
The main objectives of the SCO include:
- Strengthening mutual trust, friendship, and neighborly relations among member states.
- Promoting effective cooperation in various spheres: political, trade, economic, scientific, technical, cultural, educational, energy, transport, tourism, and environmental protection.
- Jointly maintaining peace, security, and stability in the region.
- Promoting a democratic, fair, and rational new international political and economic order.
Governance Structure:
- Its supreme decision-making body is the Council of Heads of States (CHS), which meets annually to address significant issues.
- Additionally, the Council of Heads of Government (CHG), comprising Prime Ministers, convenes once a year.
The SCO's governance includes:
- Council of Heads of States (CHS): The supreme decision-making body that meets annually.
- Heads of Government Council (HGC): Focuses on economic cooperation and budget approval.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Coordinates counter-terrorism efforts among member states.
- Standing Bodies:
- Secretariat: Located in Beijing, responsible for administrative tasks.
- Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Based in Tashkent, focuses on counter-terrorism efforts.
Cooperation with International and Regional Organizations:
SCO actively seeks partnerships with various international and regional organizations to enhance its cooperative framework. The key organizations with which the SCO collaborates include:
-
Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS):
- MoU Signed: April 12, 2005.
- Focus Areas: Security cooperation, counter-terrorism, economic collaboration, cultural exchange, and humanitarian issues.
- Objective: To ensure regional and international security, combat organized crime, and promote economic cooperation among member states.
-
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
- MoU Signed: April 21, 2005.
- Focus Areas: Combating terrorism, drug and arms trafficking, money laundering, and illegal migration.
- Objective: To promote economic cooperation and security collaboration, addressing shared challenges and enhancing mutual interests in trade and development.
-
Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO):
- MoU Signed: October 5, 2007.
- Focus Areas: Regional security, counter-terrorism, and combating drug trafficking and organized crime.
- Objective: To create a unified approach towards ensuring stability and security in the region, capitalizing on each organization’s strengths.
-
Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO):
- MoU Signed: December 11, 2007.
- Focus Areas: Economic and trade cooperation, environmental protection, tourism, and transport.
- Objective: To share knowledge and positive experiences in economic and trade practices, enhancing collaboration on regional development.
-
Conference on Interaction and Confidence-Building Measures in Asia (CICA):
- MoU Signed: May 20, 2014.
- Focus Areas: Regional conflicts, non-proliferation regimes, and responses to terrorism and transnational crime.
- Objective: To align efforts in addressing common challenges and promote peace and security across Asia.
-
International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC):
- MoU Signed: June 9, 2017.
- Focus Areas: International humanitarian law (IHL), emergency response, and humanitarian assistance.
- Objective: To enhance dialogue on humanitarian issues, promote IHL norms, and implement joint humanitarian projects.
Cooperation with the United Nations:
The SCO maintains a strategic partnership with the United Nations (UN) to facilitate broader global cooperation on security, development, and humanitarian issues. key resolutions and agreements:
-
Observer Status:
- On December 2, 2004, the UN General Assembly adopted a Resolution granting the SCO observer status in the General Assembly.
- Significance: This status allows the SCO to participate in UN sessions, enhancing its international profile and ability to engage in global discussions.
-
Regular Contacts:
- The SCO engages in regular information exchanges with the UN Secretariat and institutions based in Beijing.
- High-ranking UN officials are often invited to attend SCO summits, reflecting a commitment to dialogue and collaboration.
-
Joint Declarations:
- On April 5, 2010, a Joint Declaration on Cooperation was signed by the SCO Secretary-General and the UN Secretary-General.
- Focus: Expanding communication, information exchange, and cooperation on issues of mutual concern, particularly in counter-terrorism and sustainable development.
-
Collaborative Initiatives:
- The SCO works closely with specific UN bodies, such as the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP), on issues like drug trafficking, economic development, and humanitarian aid.
- Examples: MoUs signed with UNODC in June 2011 and with UNESCAP in August 2012 to enhance operational cooperation.
SIGNIFICANCE FOR INDIA :
- On one level, SCO membership allows India to participate in a forum which enhances its scope of cooperation with Central Asian countries, which have not had particularly close relations with India since their formation in 1991.
- It also matters for maintaining communication with major actors in the Region on common security issues.
- For example, an important permanent structure within the SCO is the Regional anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS).
- It assists members in the preparation and staging of counter-terrorism exercises, analyses key intelligence information coming in from the member states, and shares information on terrorist movements and drug trafficking.
Challenges Ahead:
- Given the current geopolitical landscape, India's relationships with China and Pakistan remain fraught with tension.
- Notably, India opted for a virtual summit during its presidency in 2023, indicating the challenges in managing inter-member dynamics within the SCO.
CONCERNS IN BRI
Bilateral issues remain unsolved:
- India & China have unresolved border issues.
- Last year, when the summit was under India’s leadership, it was hosted digitally.
- India refused to sign the paragraph which endorsed the Belt & Road Initiative (BRI)
- India & Pakistan relationship have time & again been hampered by Cross Border Terrorism.
Recent Meeting : 23rd Meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of Government:
On October 16, 2024, India’s National statement Delivered by: Dr. S. Jaishankar, External Affairs Minister of India in Islamabad
- Dr. Jaishankar congratulated Pakistan on its presidency of the SCO Council of Heads of Government for 2024 and affirmed India's support for a successful presidency.
Global Context:
- Difficult Times: Dr. Jaishankar acknowledges significant global challenges:
- 2 Major Conflicts: Ongoing geopolitical conflicts affecting global stability.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: Highlighting long-term repercussions on developing nations.
- Disruptions: Various types of disruptions include:
- Extreme Climate Events: Natural disasters impacting agriculture and livelihoods.
- Supply Chain Uncertainties: Disruptions in trade routes and production.
- Financial Volatility: Fluctuations in financial markets.
- Debt Concerns: Rising debt levels hindering development and the ability to meet Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
SCO's Charter and Objectives:
- Reflection on the Charter: Dr. Jaishankar urges members to consider Article 1 of the SCO Charter, which outlines:
- Strengthening Mutual Trust: Building confidence among member states.
- Friendship and Good Neighbourliness: Fostering positive relationships.
- Multi-faceted Cooperation: Encouraging collaboration across various sectors.
- Balanced Growth and Integration: Ensuring equitable and inclusive development.
- Conflict Prevention: Proactive measures to avoid disputes.
- Need for Honest Conversation:
- Emphasizes the necessity of understanding the reasons behind a lack of trust and cooperation.
- Highlights the importance of reaffirming commitment to the Charter for realizing cooperation benefits.
The Global Shift towards Multi-Polarity:The world is transitioning towards a multi-polar structure, creating new opportunities in:
-
- Trade: Increased cross-border commerce.
- Investment: Enhanced foreign direct investment.
- Connectivity: Improved transportation and communication networks.
- Energy Flows: More diverse energy partnerships.
Principles of Cooperation:
- Cooperation must respect each nation’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Commitment to the SCO Charter:
- Importance of Development and Stability: Development is contingent on a collective stance against 3 evil:
- Terrorism
- Extremism
- Separatism
- Importance of Development and Stability: Development is contingent on a collective stance against 3 evil:
Potential for Cooperation: Dr. Jaishankar outlines areas for substantial benefits:
-
- Industrial Cooperation: Enhancing competitiveness and labor market expansion.
- MSME Collaboration: Significant contributions to employment from small and medium enterprises.
- Investment Flows: Stimulating more investment opportunities through collective efforts.
- Logistics and Energy Efficiency: Improved processes in logistics and energy sectors.
- Environmental Protection and Climate Action: Collaborative projects addressing environmental challenges.
- Healthcare: Shared capabilities in pharmaceuticals enhancing health security.
- Cultural and Educational Exchanges: Rich avenues for collaboration in culture, education, and sports.
India's Global Initiatives: Dr. Jaishankar highlights initiatives aligned with SCO objectives:
-
- International Solar Alliance: Promoting solar energy use.
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure: Preparing nations for climate-related disasters.
- Mission LiFE: Advocating sustainable living practices.
- Promotion of Yoga and Millets: Aiming for wellness and environmental sustainability.
- Global Biofuel Alliance: Transitioning to renewable energy sources.
- International Big Cat Alliance: Protecting biodiversity.
- Domestic Successes: Mentions India's digital public infrastructure and initiatives aimed at women-led development.
Reforming Global Institutions
- Call for Reformed Multilateralism: Advocates for global institutions to adapt to the evolving order.
- UN Security Council Reform: Emphasizes the need for adequate representation of developing countries.
- SCO's Leadership Role: Reiterates the importance of the SCO advocating for such reforms.
Renewing Commitment
- Focus on Pathways Forward: He urged member states to renew their resolve to achieve SCO objectives, recognizing constraints on cooperation and mutual interests.
- Adherence to Charter Principles: Stresses the importance of following the principles articulated in the Charter.
Conclusion:
Dr. Jaishankar's statement shows the challenges faced by the SCO and the global community, underscoring the need for cooperation based on mutual respect, commitment to peace, and the goals outlined in the SCO Charter. He calls for collective efforts to tackle shared challenges, seize opportunities for collaboration, and advocate for necessary reforms in global governance structures.
UPSC PYQ [Year: 2019]
Q: Consider the following statements regarding the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO):
- India became a full member of SCO in 2017.
- SCO was originally formed by China and Russia.
- The SCO is focused primarily on economic cooperation, not security.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) All of the above
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Probable MCQ for Prelims 2025
Q: Which of the following countries joined SCO in 2024?
a) Belarus
b) Mongolia
c) Afghanistan
d) Turkey
Answer: a) Belarus
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




