Introduction
- The IT sector, short for Information Technology sector, refers to the industry that deals with the use of computers, software, and telecommunications equipment to manage, process, and store data.
- The IT sector includes a wide range of businesses and services, including hardware and software development, networking and telecommunications, internet services, e-commerce, digital content creation, and IT consulting.
- The sector has grown rapidly in recent years due to the increasing use of computers and the internet in both personal and business settings. The IT sector is a key driver of economic growth and innovation, and has transformed many aspects of modern life, including the way we work, communicate, and access information.
Facts about IT sector of India
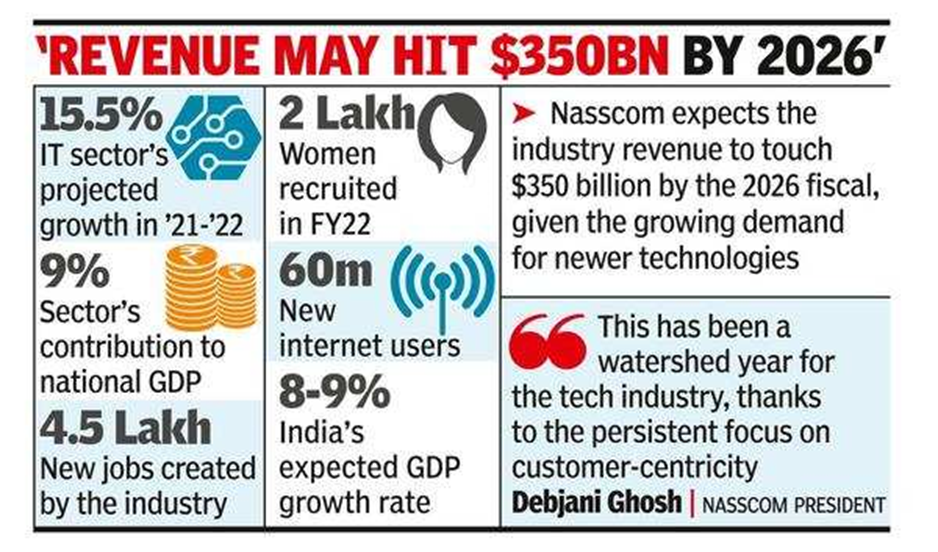
- The IT & BPM sector has become one of the most significant growth catalysts for the Indian economy, contributing significantly to the country’s GDP and public welfare. The IT industry accounted for 7.4% of India’s GDP in FY22, and it is expected to contribute 10% to India’s GDP by 2025.
- As innovative digital applications permeate sector after sector, India is now prepared for the next phase of growth in its IT revolution. India is viewed by the rest of the world as having one of the largest Internet user bases and the cheapest Internet rates, with 76 crore citizens now having access to the internet.
- According to National Association of Software and Service Companies (Nasscom), the Indian IT industry’s revenue touched US$ 227 billion in FY22, a 15.5% YoY growth.
- According to Gartner estimates, IT spending in India is expected to increase to US$ 101.8 billion in 2022 from an estimated US$ 81.89 billion in 2021.
- Indian software product industry is expected to reach US$ 100 billion by 2025. Indian companies are focusing on investing internationally to expand their global footprint and enhance their global delivery centres.
Major achievements of India in the IT
- IT Services: India is a leading provider of IT services to global companies. Indian IT companies, such as TCS, Infosys, and Wipro, are among the largest IT service providers in the world. These companies provide a range of IT services, including software development, system integration, and IT consulting.
- IT Outsourcing: India is a major destination for IT outsourcing. Many global companies, including Microsoft, IBM, and Accenture, have established development centers and service centers in India. For example, Microsoft has a development center in Hyderabad, India, which is one of its largest centers outside the US.
- IT startups: India has a vibrant startup ecosystem in the IT sector. Companies such as Flipkart, Ola, Paytm, and Zomato have become household names in India and have gained global recognition. For example, Paytm is a digital wallet and payment gateway that has become one of the leading payment platforms in India.
- Mobile app development: India has emerged as a hub for mobile app development, with many Indian companies and startups developing innovative mobile apps for various industries and sectors. For example, Practo is a mobile app that provides online doctor consultations, appointments, and medical records.
- IT education and training: India has a large pool of skilled IT professionals, with many Indian universities and institutes offering IT education and training. Indian IT professionals are highly sought after in the global job market. For example, the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) are among the most prestigious engineering institutes in the world and have produced many successful IT professionals.
Applications of IT technology in the Indian economy
- E-commerce: Online shopping platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, and Snapdeal have transformed the way Indians shop. These platforms use IT technology to connect buyers and sellers and enable secure transactions.
- Online banking: Banks like ICICI, HDFC, and SBI have developed robust online banking systems that allow customers to access their accounts, transfer funds, pay bills, and more. These systems use IT technology to ensure security and reliability.
- Digital payments: The Indian government’s push towards a cashless economy has led to the widespread adoption of digital payment platforms like Paytm, Google Pay, and PhonePe. These platforms use IT technology to facilitate secure and instant transactions.
- Healthcare: IT technology is being used to improve healthcare in India through telemedicine, electronic health records, and medical imaging systems. For example, companies like Practo and Apollo Hospitals offer online consultation services, and healthcare providers use IT systems to store and share patient data.
- Education: IT technology is being used to enhance education in India through e-learning platforms like BYJU’S, Simplilearn, and Udacity. These platforms use IT technology to deliver engaging and interactive learning experiences to students.
- Agriculture: IT technology is being used to improve agricultural productivity in India through precision farming, crop monitoring, and weather forecasting. For example, companies like CropIn and AgroStar offer farmers real-time data and insights to help them make informed decisions.
Major challenges to Indian IT sector
- New skills shortage: Despite having a large pool of graduates, the Indian IT sector faces a talent shortage, particularly in emerging areas like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). According to a report by NASSCOM, the Indian IT industry will need to reskill about 1.5 to 2 million of its employees to stay competitive. Additionally, India produces only 2.5% of global research output in AI.
- Increasing competition: The Indian IT sector faces increasing competition from other emerging economies like China, the Philippines, and Vietnam. According to a report by NASSCOM, the Indian IT industry’s share in the global IT services market has decreased from 58% in 2008 to 56% in 2019.
- Data privacy and security: India’s data privacy and security laws are still evolving and may not be at par with global standards. This can lead to a lack of trust in Indian IT services by foreign clients. According to a report by DSCI, India ranks 10th out of 50 countries in the Global Privacy Index 2020.
- Infrastructure challenges: India’s IT sector faces infrastructure challenges such as power cuts, inadequate bandwidth, and poor physical connectivity. According to the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index 2018, India ranks 44th out of 160 countries in terms of infrastructure quality.
- Protectionist policies: Protectionist policies by other countries, especially the US, can have a significant impact on the Indian IT sector. According to a report by NASSCOM, the US accounted for 60% of the Indian IT industry’s revenue in 2020.
Reforms needed in the Indian IT sector
- Skilling and upskilling: India needs to focus on skilling and upskilling its workforce to meet the changing demands of the IT industry. According to a report by NASSCOM, only 40% of engineering graduates in India are employable in the IT industry. To address this gap, the Indian government has launched various initiatives like Skill India and Digital India to provide training and skill development to its citizens.
- Research and development: India needs to invest more in research and development (R&D) to develop new technologies and stay competitive in the global IT market. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), India ranks 48th in the Global Innovation Index 2021, up from 52nd in 2020. To address this, the Indian government has increased the budget for R&D and launched various initiatives like the Atal Innovation Mission to promote innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Regulatory environment: India needs to create a favorable regulatory environment for the IT industry to attract investment and foster innovation. According to the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business Index 2021, India ranks 63rd out of 190 countries in terms of ease of starting a business. To address this, the Indian government has launched various initiatives like Startup India and Make in India to promote entrepreneurship and investment in the IT sector.
- Data privacy and security: India needs to strengthen its data privacy and security laws to protect sensitive information and ensure trust in the IT sector. According to a report by DSCI, India ranks 10th out of 50 countries in the Global Privacy Index 2020. To address this, the Indian government has introduced the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019 to regulate the collection, storage, and use of personal data.
Some of the major schemes related to IT sector

- PLI scheme: With the objective to boost domestic manufacturing, investments and export in the telecom and networking products Department of Telecommunications (DoT) notified the “Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme” on 24th February 2021.The PLI Scheme will be implemented within the overall financial limits of ₹ 12,195 Crores only (Rupees Twelve Thousand One Hundred and Ninety-Five Crore only) for implementation of the Scheme over a period of 5 years.
- Digital India: Launched in 2015, the Digital India programme aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. The initiative includes various projects like e-governance, broadband connectivity, digital literacy, and digital infrastructure.
- National Cyber Security Policy, 2013: The Policy’s goal is to create safe and resilient cyberspace for citizens, businesses, and the Government.
- Skill India: Launched in 2015, the Skill India initiative aims to provide vocational training and skill development to India’s youth to make them employable in various industries, including IT. The initiative includes various training programmes, certification courses, and apprenticeship schemes.
- Reskilling Revolution initiative: The World Economic Forum (WEF) announced on Wednesday that more than 350 million people are being reached with better skills, jobs and education through commitments made as part of its Reskilling Revolution initiative, three years after launching at its Annual Meeting in Davos. The initiative includes Indian IT companies also.
- Atal Innovation Mission: Launched in 2016, the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) aims to promote innovation and entrepreneurship in India. The initiative includes various programmes like Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centers, and Atal New India Challenges to provide funding, mentoring, and incubation support to startups and innovators in the IT sector.
These schemes and initiatives have played a crucial role in promoting the growth and development of the IT sector in India and have helped to establish the country as a global IT hub.






